Meat safety and hygiene are critical factors in ensuring the quality and safety of the meat we consume. With the increasing concern about foodborne illnesses and contamination, it is essential to understand the best practices and guidelines for proper meat handling, storage, and preparation.
The Importance of Meat Safety
Meat, being a highly perishable food product, can be a breeding ground for bacteria and pathogens if not handled and stored properly. Contaminated meat can lead to foodborne illnesses, posing serious health risks to consumers. Therefore, ensuring meat safety is crucial to prevent the spread of foodborne diseases and maintain public health.
Understanding Meat Hygiene
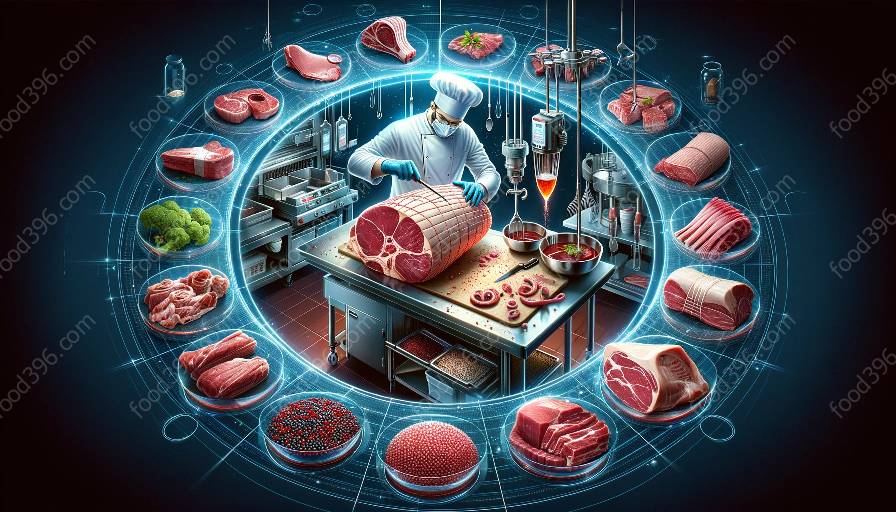
Meat hygiene involves the application of proper sanitation and cleanliness measures throughout the meat production and handling process. This includes maintaining a clean and hygienic environment in slaughterhouses, meat processing facilities, and retail outlets, as well as practicing good personal hygiene when handling meat. Hygienic practices are essential to prevent cross-contamination and the spread of bacteria, ensuring that meat remains safe for consumption.
Best Practices for Meat Safety and Hygiene
When it comes to meat safety and hygiene, there are several key best practices that should be followed at every stage, from processing to consumption:
- 1. Meat Handling and Storage: Properly handle and store meat products according to recommended guidelines to maintain freshness and prevent contamination. This includes maintaining appropriate temperatures during storage and transport, as well as separating raw and cooked meats to prevent cross-contamination.
- 2. Personal Hygiene: Those involved in meat handling, including workers in the meat industry and consumers, should practice good personal hygiene, such as handwashing and the use of protective clothing, to prevent the spread of bacteria and pathogens.
- 3. Cleaning and Sanitization: Regular cleaning and sanitization of meat processing equipment, facilities, and utensils are crucial to prevent the growth and spread of harmful bacteria. Proper sanitation measures help maintain a hygienic environment throughout the meat supply chain.
- 4. Cooking and Handling Temperatures: Ensure that meat products are cooked to the appropriate internal temperatures to kill any harmful bacteria. Using food thermometers is recommended to verify that meats are cooked to the proper temperatures.
Regulatory Guidelines and Standards
Meat safety and hygiene are governed by regulatory guidelines and standards established by food safety authorities and organizations. These regulations outline the requirements and best practices for meat producers, processors, and distributors to ensure compliance with safety and hygiene standards. Additionally, certifications and audits are often conducted to verify that meat facilities adhere to the necessary protocols to maintain food safety and quality.
Consumer Awareness and Education
Ensuring meat safety and hygiene also involves educating consumers about the best practices for handling and preparing meat at home. This includes proper storage, cooking, and handling techniques to minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses. By raising awareness and providing education on meat safety, consumers can make informed decisions to protect themselves and their families from food-related hazards.
Advancements in Meat Science
Advancements in meat science play a significant role in enhancing meat safety and hygiene practices. Research and innovation in areas such as food microbiology, food safety technologies, and packaging solutions contribute to improving the overall safety and quality of meat products. By leveraging scientific knowledge and technological advancements, the meat industry can continue to elevate its standards for safety and hygiene.
Conclusion
Meat safety and hygiene are essential elements in ensuring the quality, safety, and integrity of meat products. By following best practices, adhering to regulatory standards, and staying informed about advancements in meat science, both industry professionals and consumers can contribute to the maintenance of food safety and public health. With a collective effort to prioritize meat safety and hygiene, we can minimize the risks associated with meat handling and consumption, ultimately safeguarding the well-being of individuals and communities.